-ˋˏ ༻ 2 ༺ ˎˊ-
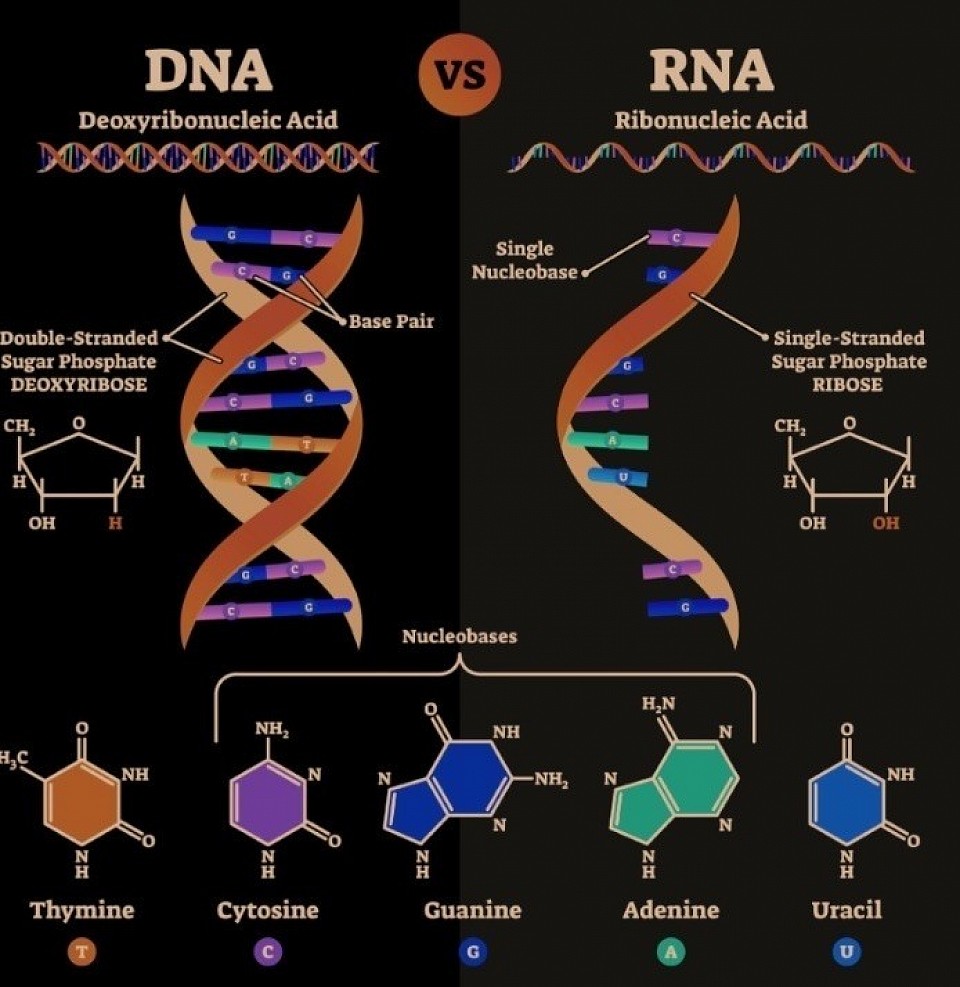
Nucleotides
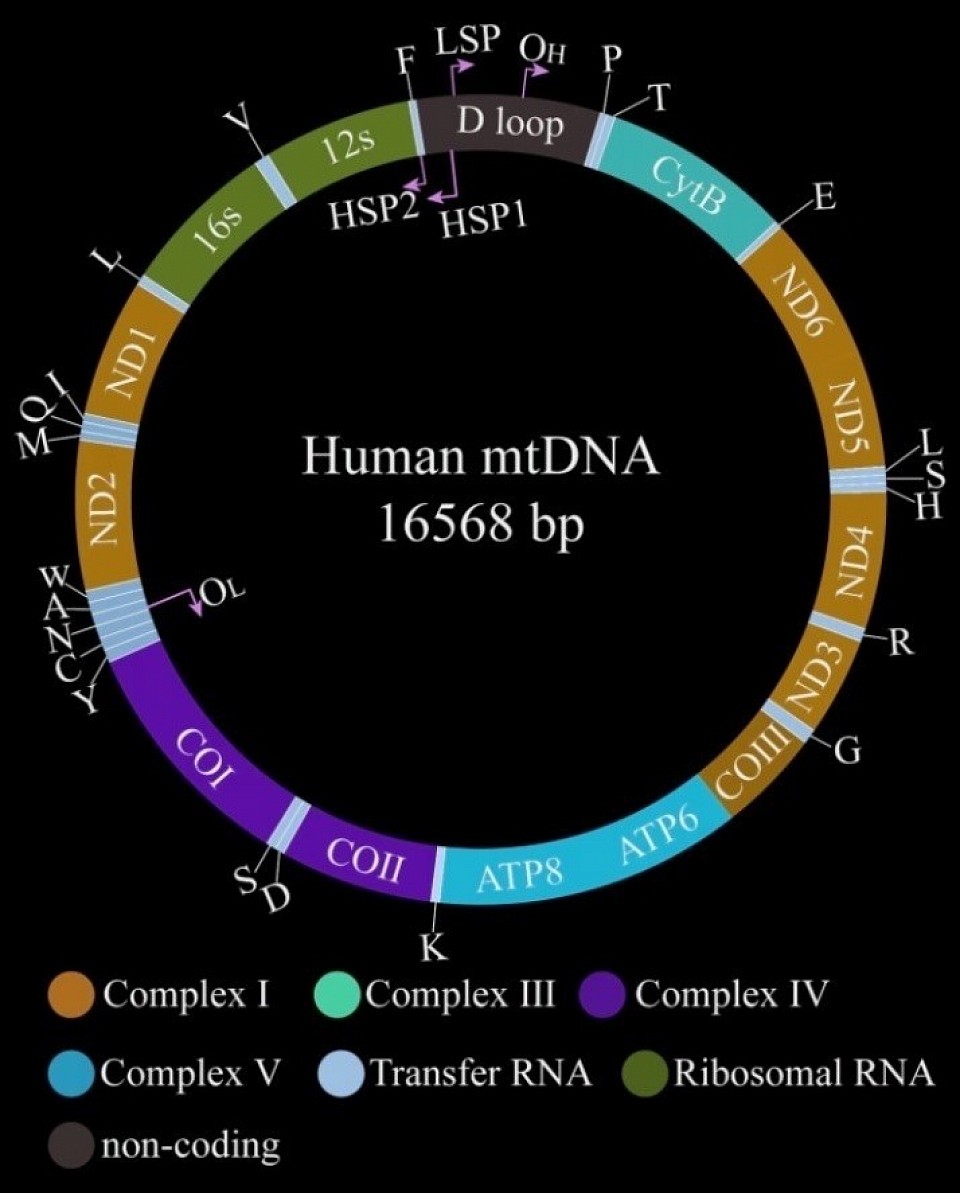
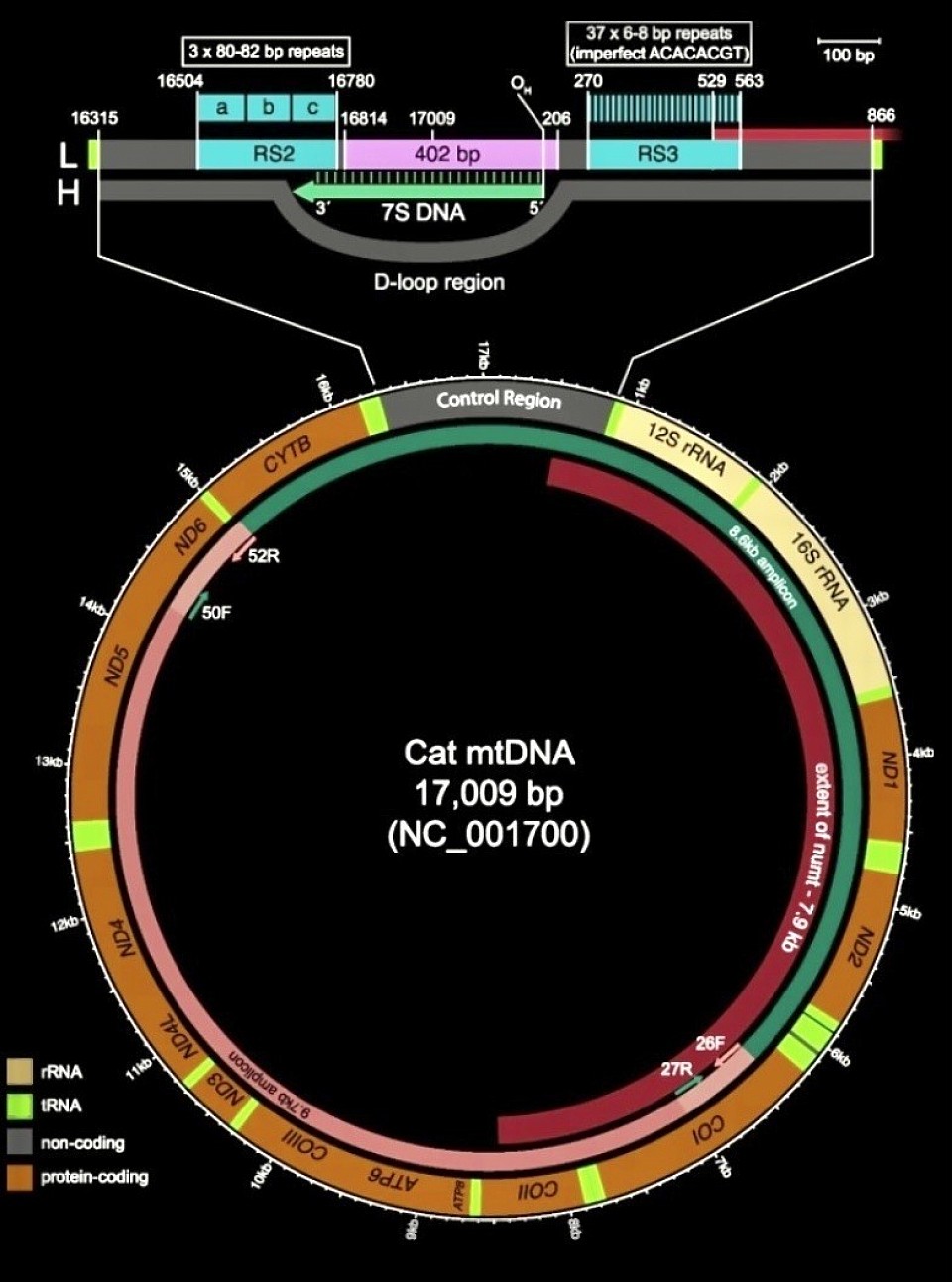
How nucleotides shape the culture
The Culture of the Laminae
──── ·:*¨༺ ♱✮♱ ༻¨*:· ────
Dorsal (Posterior) Horn:
contains neurons that receive somatosensory information from the body, which is then transmitted via the ascending pathways
It receives sensory information from the body via the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves
The dorsal root emerges from the spinal cord and travels to the dorsal root ganglion (DRG), a collection of nerve cell bodies
Dorsal Horn Neurons:
local interneurons:
These are a specific type of interneuron that connect and process information within a small, localized area of the central nervous system, such as the spinal cord
typically have short axons and only interact with neighboring neurons
and projection neurons:
specifically within the dorsal horn, are the output cells that relay processed sensory information, including pain and itch, from the spinal cord to the brain, with populations found in lamina I and deeper laminae
process this sensory information, including pain, temperature, touch, and proprioception (awareness of body position)
The dorsal root continued
The processed sensory information is then relayed to the brain via, ascending pathways (e.g., the dorsal column-medial lemniscal pathway)
deal with the conscious appreciation of fine touch, two-point discrimination, conscious proprioception, and vibration sensations from the entire body except for the head
The dorsal horn contains various neurotransmitters that transmit peripheral information to spinal cord neurons,
excitatory:
Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood of a neuron firing an action potential by depolarizing the postsynaptic membrane
meaning making the inside of the cell less negative (more positive) relative to the outside
When a neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, it can cause ion channels to open, allowing positively charged ions (like sodium, Na+) to flow into the cell
neurotransmitters including:
glutamate:
acts as the primary excitatory neurotransmitter, crucial for spinal excitatory synaptic transmission, pain perception, and sensory information processing
inhibitory:
prevent or decrease the likelihood of a nerve cell firing an action potential, thus playing a crucial role in regulating neuronal activity and preventing overexcitation
GABA:
GABA is an amino acid that functions as a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger
glycine:
Glycine exerts its inhibitory effects by binding to specific glycine receptors (GlyRs), which are ionotropic receptors that open chloride channels
When glycine binds to GlyRs, chloride ions flow into the neuron, causing hyperpolarization and inhibiting neuronal firing
Neurotransmitters:
nitric oxide (NO):
a gas, acts as a unique neurotransmitter, diffusing across cell membranes and affecting nearby cells, rather than being stored and released like conventional neurotransmitters. It plays a role in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory, and can also have neurotoxic and neuroprotective effects.
prostaglandins:
while not neurotransmitters themselves, are potent lipids that act as modulators of neurotransmission, influencing the release and action of neurotransmitters like norepinephrine. They are considered local hormones or autacoids, playing a role in various physiological functions, including inflammation and pain
adenosine triphosphate (ATP):
acts as a neurotransmitter and a cotransmitter in both the central and peripheral nervous systems, mediating various functions through activation of P2X and P2Y receptors
endogenous opioids:
also known as neuropeptides, produced naturally in the body that act as neuromodulators, influencing pain, emotion, reward, and other functions by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord
monoamines (serotonin and norepinephrine)
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine): Regulates mood, sleep, appetite, and other functions
Norepinephrine (also called noradrenaline):Plays a role in alertness, arousal, and the "fight-or-flight" response
𖤓
Folklore
Folktales explaining the first region of Organelle
──── ·:*¨༺ ♱✮♱ ༻¨*:· ────
Ventral (Anterior) Horn:
largely contains motor neurons that exit the spinal cord
contains the cell bodies of motor neurons, which send axons via the ventral roots to innervate skeletal muscles
ventral roots are bundles of axons that carry efferent (motor) signals from the spinal cord to the body's skeletal muscles, emerging from the spinal cord laterally towards the anterior surface
It's primarily a motor region, meaning it contains the neurons responsible for sending signals that cause muscles to contract
The ventral horn contains two types of lower motor neurons:
alpha motor neurons
which supply the extrafusal muscle fibers with nerves
outside the muscle spindle - a sensory receptor
gamma motor neurons
which supply the intrafusal muscle fibers with nerves
located within a muscle spindle - a sensory receptor
Sensory receptors are specialized cells that detect stimuli from the internal or external environment and convert them into electrical signals for the nervous system to interpret
Part of the body’s Proprioception system
the ability to sense the position and movement of our body parts, mediated by specialized receptors (proprioceptors) in muscles, tendons, and joints, allowing us to move and maintain balance without relying solely on vision
Specialized sensory receptors, like muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs, are located in muscles, tendons, and joints
The brain processes this information, creating a "mind's eye" view of our body's position and movement
The axons of these motor neurons exit the spinal cord via the ventral roots, which are part of the spinal nerves
𖤓
Folklore
Folktales explaining the second region of Organelle
⋆˚𝜗𝜚˚⋆
Folklore
Folktales explaining the first circle
Folklore
Folktales explaining the second circle
━━━━━━━•°•°•❈•°•°•━━━━━━━
The World Of The Dead
What is experienced in the world of the dead is that everything to be built is in reverse compared to the world of the living
Meiosis in reverse, Chromosomes in reverse, nucleotides in reverse, you get the picture